1. The Foundation of YAG in Laser Technology
The evolution of laser technology is a fascinating journey marked by continuous innovations. One such pivotal development is the introduction of Yttrium Aluminum Garnet, commonly referred to as YAG. This unique crystalline material has proven to be a game-changer, reshaping how lasers are perceived and utilized across diverse sectors.
In the early days of laser technology, there was a relentless quest for materials that could provide a stable and efficient lasing medium. The pursuit was not just about power; it was about precision, durability, and versatility. As lasers began to find their footing in medical surgeries, high-precision industrial processes, and scientific research, the demand for a superior lasing medium intensified.
Enter YAG. Its inherent properties, especially the structural advantages of Yttrium Aluminum Garnet, promised unparalleled performance. This wasn’t just another material on the block; it had the potential to revolutionize the laser landscape.
Its adoption was not immediate but rather a progressive recognition of its capabilities. By the time the late 20th century rolled around, YAG had firmly established itself. Researchers and industry experts identified its potential to amalgamate the robustness of its crystalline structure with exceptional lasing capacities. The fusion of these two components resulted in the creation of a solid-state laser system, a significant departure from earlier laser types.
This wasn’t merely a technical upgrade; it was a transformative shift. The newly developed YAG lasers could deliver high power outputs without compromising on precision. Their efficiency was unmatched, capable of sustained performance under rigorous conditions, setting new standards in the industry.
Moreover, their versatility ensured their relevance across various fields. From delicate medical procedures where precision was paramount, to demanding industrial applications where durability and power were key, YAG lasers showcased unmatched prowess. Their introduction not only filled an existing void in laser technology but also opened doors to possibilities previously unimagined. The future of lasers had been redefined, with YAG lasers at its heart.

2. Diving into Nd:YAG Solid-State Lasers
The world of lasers is vast and diversified, with various materials and technologies employed to achieve specific outcomes. Among these, the Neodymium-doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet, more commonly referred to as Nd:YAG, stands out. This solid-state laser is a testament to the relentless innovation in laser technology. By introducing neodymium ions into the YAG crystal, scientists were able to harness a new level of performance, further enhancing the already impressive attributes of YAG lasers.
What truly sets Nd:YAG lasers apart is their resilience. These lasers are designed to function under challenging conditions, be it in high-temperature environments, under immense pressure, or in situations requiring constant and prolonged usage. Their durability ensures a consistent output, making them a preferred choice for a multitude of applications.
Moreover, their adaptability is a defining trait. While the fundamental design is based on the YAG architecture, the infusion of neodymium ions adds a unique layer of versatility. This not only amplifies its power but also expands its utility across a broader spectrum.
One of the prominent features of Nd:YAG lasers is their incredible gain cross-section. In simpler terms, this means that these lasers can amplify light remarkably efficiently. Such a trait is invaluable, especially in applications where a high degree of amplification is essential without the need for excessive energy inputs.
The coherent beam produced by Nd:YAG lasers is another highlight. Coherence ensures that the light waves are in phase, resulting in a beam that can be focused on a very small spot with high precision. This precision opens doors to applications that require intricate detailing, from microsurgeries to intricate engraving on materials.
One cannot overlook the high peak powers these lasers can achieve. This makes them perfectly suited for applications demanding intense and swift bursts of energy. Whether it’s for breaking down materials in industrial processes or for medical treatments requiring instant energy surges, Nd:YAG lasers prove their mettle.
Furthermore, their ability to emit in the infrared region, specifically at 1064 nm, brings about its own set of advantages. This wavelength ensures deep penetration, making it effective in processes like cutting and engraving, especially on materials that are typically challenging to work with.
Lastly, the inherent flexibility of Nd:YAG lasers is commendable. Their design allows for tuning to produce different wavelengths. This adaptability ensures they can be customized for various requirements, further solidifying their position as one of the most versatile lasers in the market.
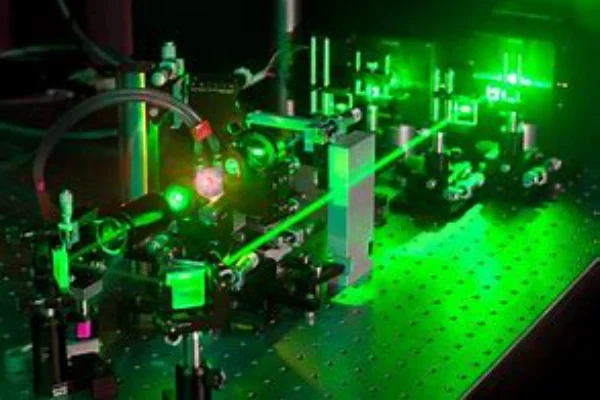
3. YAG in High-Power Industrial Applications
The industrial world, characterized by its relentless pace and demand for precision, has always been in pursuit of technologies that can enhance efficiency and accuracy. YAG lasers have emerged as a promising solution, meeting the rigorous demands of various industries. These lasers are not merely tools; they represent a transformative shift in how industrial processes are approached and executed.
Manufacturing units, workshops, and factories are often environments of extreme conditions. Whether it’s the searing heat of foundry units or the high-pressure zones of metal workshops, the equipment used needs to be resilient. YAG lasers, with their robust build and consistent output, have become an invaluable asset in such environments. They function seamlessly, regardless of external conditions, ensuring that the workflow remains uninterrupted.
In the realm of metal fabrication, the margin for error is incredibly slim. Precision is not just a desirable trait; it’s an absolute necessity. YAG lasers have risen to this challenge, offering a level of accuracy that’s unparalleled.
Consider metal cutting, for instance. Traditional methods often led to uneven edges, considerable material wastage, and a prolonged process. YAG lasers, with their high-power beams, have revolutionized this. They can focus their energy on incredibly small areas, slicing through metals with a neat finish and remarkable speed. This not only ensures a quality end product but also reduces material wastage significantly.
Welding, a critical process in metal fabrication, has also witnessed a transformation with YAG lasers. Welding requires the fusion of metal pieces, and traditional methods could lead to weak joints or structural vulnerabilities. With YAG lasers, the welding process is not only faster but also results in stronger, more reliable joints. The precision ensures that the weld is consistent throughout, enhancing the durability of the final product.
Beyond the heavy-duty tasks of cutting and welding, YAG lasers have found their niche in the delicate art of marking and engraving. Industries require various components to be marked for identification, be it serial numbers, barcodes, or intricate designs. The traditional methods were often time-consuming and lacked precision.
YAG lasers, with their pinpoint accuracy, have changed the game. Whether it’s engraving a detailed design on a ceramic piece or imprinting a barcode on a metal component, the lasers ensure that the mark is clean, clear, and durable. This has not only improved the aesthetic quality of engraved products but also enhanced the efficiency of the marking process, saving industries both time and resources.

4. YAG in the Realm of Medical Lasers
In the ever-evolving landscape of medical technology, YAG lasers have emerged as a beacon of innovation and efficiency. They have ushered in a new era of medical procedures, combining the precision of laser technology with the delicacy required in medical applications. This powerful synergy has resulted in treatments that are less invasive, more accurate, and remarkably effective.
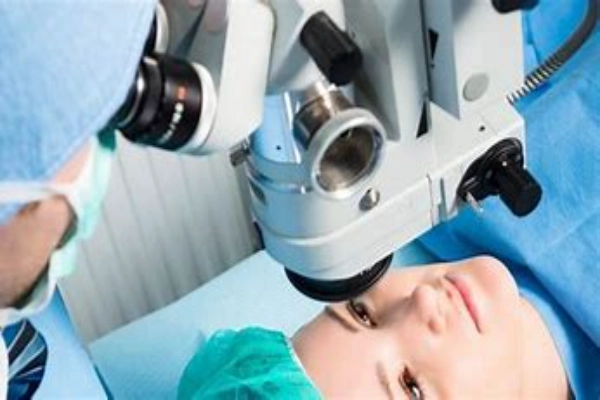
Within the realm of ophthalmology, YAG lasers have carved a niche for themselves. Cataract surgery, a procedure that millions undergo each year, occasionally results in a complication known as posterior capsule opacification. This clouding effect can compromise vision, often requiring further intervention.
Enter YAG lasers, which have become the gold standard in treating this complication through a procedure called posterior capsulotomy. With their precision, the lasers can create a small opening in the clouded capsule, restoring clarity of vision, all while ensuring minimal discomfort and quicker recovery times for patients.
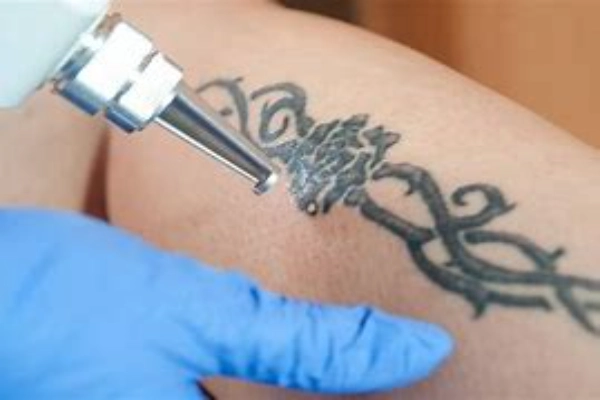
But the medical wonders of YAG lasers aren’t confined to just ophthalmology. The field of dermatology, dedicated to the study and treatment of skin conditions, has also harnessed the power of these lasers. Tattoo regret is a common sentiment, and YAG lasers provide an efficient solution for tattoo removal.
Their ability to target the tattoo ink particles without affecting the surrounding skin ensures effective removal with minimal scarring. Similarly, for vascular lesions – unsightly blood vessels that can appear on the skin’s surface – YAG lasers offer a targeted treatment approach. The lasers work by emitting wavelengths that are absorbed by the blood vessels, causing them to shrink and eventually disappear. All of this is achieved with a keen focus on preserving the surrounding tissues, ensuring that patients receive the best results with the least side effects.
In essence, whether it’s restoring vision clarity or rejuvenating skin, YAG lasers have transformed the medical field, offering hope, efficiency, and optimal outcomes for countless patients.
5. The Science Behind YAG’s Efficiency
The remarkable efficiency of YAG lasers is deeply rooted in their unique composition and crystalline makeup. At the heart of this efficiency is the gain cross-section, a measure indicating a material’s capability to amplify light. YAG’s exceptional structure allows for unparalleled light amplification, positioning it leagues ahead in the laser world. But efficiency isn’t its only hallmark; the durability of YAG crystals ensures sustained performance even under rigorous operations. This resilience translates to a longer lifespan and minimal maintenance, affirming YAG’s reputation as both a powerful and reliable laser medium.
Conclusion
The footprint of YAG in laser technology is expansive and undeniable. From industrial behemoths to critical medical procedures, YAG lasers have showcased their supremacy through consistent performance, unmatched efficiency, and adaptable utility. As technology evolves, the reliance on YAG’s exceptional properties will undoubtedly remain a cornerstone in the realm of laser applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 1. What is the main advantage of using YAG in lasers?
- YAG lasers offer unparalleled efficiency and power, making them ideal for a wide range of applications, from industrial to medical.
- 2. How does Nd:YAG differ from standard YAG?
- Nd:YAG is a type of YAG laser doped with neodymium ions, enhancing its lasing properties and providing flexibility in terms of wavelengths.
- 3. In which medical field is YAG predominantly used?
- YAG lasers have found profound use in ophthalmology, especially in procedures like posterior capsulotomy.
- 4. What ensures the durability of YAG lasers in industrial applications?
- The robust crystalline structure of YAG ensures its durability, even under strenuous operations.
- 5. Why is the gain cross-section of YAG important?
- The gain cross-section determines the ability of the laser material to amplify light. YAG’s exceptional gain cross-section ensures powerful and efficient lasing.

Frank
Frank graduated from the University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, majoring in optics. As a technical engineer at Crylink Company, he deeply understands crystal materials and laser components.
Related Video(s) with this Article
Related Product(s) with this Article
Related Application(s) with this Article
