Introduction
In the continuous development of laser technology, as the demand for high – performance lasers equipped with Er,Yb:glass+Co:spinel bonding crystals in various application fields is increasing day by day, the thermal lens effect caused by laser pumping seriously hinders the further improvement of laser performance. Against this backdrop, Er,Yb:glass+Co:spinel bonding crystals have emerged as an important research direction for solving the thermal lens effect problem.
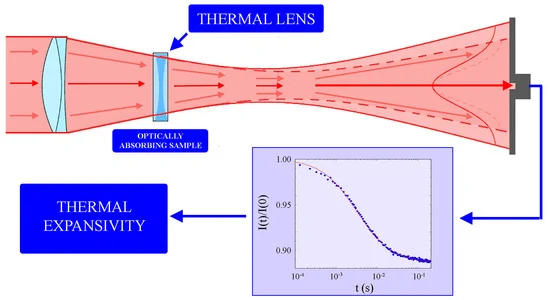
Thermal Lens Effect: An Obstacle to Laser Performance Improvement
When a laser propagates in a medium, the pumping process causes the medium to absorb energy and convert it into heat. For traditional laser gain media, this non-uniform heat distribution leads to changes in the refractive index of the medium, as if a lens is formed in the laser propagation path, which is the thermal lens effect. The thermal lens effect deteriorates the quality of the laser beam, causing the laser spot to deform and diverge, thereby reducing the focusing ability and energy transmission efficiency of the laser.
In high-power laser application scenarios, such as laser processing, laser medicine, and high-resolution spectral analysis in scientific research, the negative impact of the thermal lens effect is extremely prominent, greatly limiting the application scope and effectiveness of laser technology.
Structure and Principle of Er,Yb:glass+Co:spinel Bonding Crystals
Er,Yb:glass+Co:spinel bonding crystals adopt an innovative structural design, combining Er,Yb:glass and Co:spinel ingeniously through a special bonding process. Among them, Er,Yb:glass serves as the laser gain medium. Under the action of pumping light, it can achieve population inversion and generate laser radiation. Co:spinel has unique thermal and optical properties.
From a thermal perspective, Co:spinel has good thermal conductivity. After being bonded with Er,Yb:glass, it can effectively conduct away the heat generated by Er,Yb:glass during the laser pumping process, significantly reducing the temperature gradient inside Er,Yb:glass and thus minimizing the influence of the thermal lens effect. From an optical point of view, the optical properties of Co:spinel match those of Er,Yb:glass. While ensuring the normal transmission and gain of the laser, it will not introduce additional optical losses or interference. This well-designed bonding structure constructs an efficient “heat dissipation and stable transmission system” for the laser.

Advantages of Bonding Crystals in Reducing the Thermal Lens Effect
Significantly Improve Beam Quality
By reducing the thermal lens effect, Er,Yb:glass+Co:spinel bonding crystals can maintain good focusing and low divergence of the laser beam. In the field of laser processing, this means that more precise and accurate material cutting and welding can be achieved, improving processing accuracy and quality. For example, in the micro-nano processing field, smaller and higher-precision microstructures can be fabricated, promoting the development of industries such as semiconductor chip manufacturing and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS).
Increase Laser Output Power
The weakening of the thermal lens effect enables the laser medium to absorb pumping light energy more effectively, reducing energy loss and the proportion of energy converted into heat. Therefore, the bonded crystals can operate stably at higher pumping powers, achieving higher laser output powers. In laser medicine, higher powers can be used to treat some diseases more efficiently, such as deep tissue laser surgery, improving treatment effects and efficiency.

Enhance System Stability
Stable laser output is crucial for many applications. After Er,Yb:glass+Co:spinel bonded crystals reduce the thermal lens effect, the unstable laser output phenomenon caused by thermal-induced optical performance fluctuations is reduced. In scientific research experiments, a stable laser light source can ensure the accuracy and repeatability of experimental data, providing reliable technical support for cutting-edge fields such as optical research and quantum computing.
Application Prospects and Challenges
Currently, Er,Yb:glass+Co:spinel bonded crystals have shown great application potential in many fields. In the military field, they can be used in high-resolution lidar systems to improve the accuracy of target detection and identification. In the communication field, they can be used as high-performance optical signal emitters to increase the transmission distance and capacity of fiber optic communication. However, the widespread application of these bonded crystals still faces some challenges. On the one hand, the complexity and high-precision requirements of the bonding process result in high production costs, limiting their large-scale popularization. On the other hand, further optimizing the performance of the bonded crystals, such as improving their stability in extreme environments, remains a problem that researchers need to overcome.

Conclusion
In conclusion, Er,Yb:glass+Co:spinel bonded crystals have demonstrated excellent performance and potential in suppressing the thermal lens effect of laser pumping. Although facing many challenges, with the continuous progress of materials science and processing technology, it is expected to become a key factor promoting the development of laser technology in the future, bringing innovative changes and breakthroughs to many fields.

Frank
Frank graduated from the University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, majoring in optics. As a technical engineer at Crylink Company, he deeply understands crystal materials and laser components.
Related Video(s) with this Article
Related Product(s) with this Article
Related Application(s) with this Article
