KNbO3

KNbO3 (Potassium Niobate) crystal (KN for short) is one of the very important nonlinear optical crystals. Its nonlinear optical quality factor, d2 /n3, ranks first among all oxide crystals. The average refractive index of KN is 2.2. The theoretical value of reflectivity is 14%. The theoretical transmittance is 86%.
The crystal is chemically stable, has a large nonlinear optical coefficient, and direct frequency doubling (101 mW) of a semiconductor 860 nm laser has yielded nearly 40 mW of 430 nm blue light. Due to its special properties, the KN crystal is important in developing microlasers for this new application. The realization of blue lasers is a top priority, and KN crystals are one of the ideal materials for generating second harmonics and realizing blue lasers.
Features of KNbO3 (Potassium Niobate) Crystal:
- Millisecond response time
- Very low scattering loss
- Large nonlinear optical coefficient
- High nonlinear optical coefficient
- Excellent photorefractive properties
- High stability under light irradiation
- Favorable phase matching characteristics
Physicochemical Properties
| Chemical Formula | KNbO3 |
| Crystal Structure | Rhombic,mm2 |
| Lattice Constant | a = 5.6896Å, b = 3.9692Å, c = 5.7256Å |
| Mass Density | 4.617 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 1333 K |
| Curie Temperature | 498 K |
| Distribution of dielectric axis and crystallinity axis | X, Y, Z ⇒ b, a, c |
| Specific heat CP at P = 0.101325MPa | cp= 767 J/kgK |
| Thermal Conductivity | κ > 3.5 W/mK |
| Thermal Expansion | aa=5.010×10-6 /℃; ab=1.410×10-5/℃; ac=5.010×10-7/℃ |
Nonlinear Optical Properties
| Attribute | Numerical |
| Nonlinear Optical Coefficient | d31=-15.8 pm/V, d32=-18.3 pm/V @ 1064 nm |
| Shortest SHG Wavelength | 425 nm(Type I NCPM, y-cut or a-cut) |
| Type I SHG has an acceptance angle of 1064 nm | Dq = 0.24 mrad / cm(internal) |
| The acceptance temperature of type I SHG is 1064 nm | DT=0.3 ℃/cm |
Linear Optical Properties
| Attribute | Numerical |
| Transparent Range | 400-5500 nm |
| IR Cutoff Wavelength | 5.5 μm |
| Absorb Losses | <=1%/cm @1064 nm |
| Damage Threshold | <= 4 J/cm2 @527 nm(500ps,Single Pulse) |
| <= 6 J/cm2 @1054 nm(700ps,Single Pulse) |
Phase Matching Angle Experimental Value (T=293K)
| Interaction Wavelength[μm] | φexp [deg] | θexp [deg] |
| XY Plane,θ=90° | ||
| SHG, e + e ⇒ o | ||
| 0.946 ⇒ 0.473 | ≈30 | |
| 4.7599 ⇒ 2.37995 | 69.9 | |
| YZ Plane, φ = 90° | ||
| SHG, o + o ⇒ e | ||
| 0.86 ⇒ 0.43 | 83.5 | |
| 0.89 ⇒ 0.445 | 70.7 | |
| 0.92 ⇒ 0.46 | 64 | |
| 0.94 ⇒ 0.47 | 60.5 | |
| 1.0642 ⇒ 0.5321 | 46.4 | |
| 1.3188 ⇒ 0.6594 | 30.6 | |
| 1.3382 ⇒ 0.6691 | 29.7 | |
| 3.5303 ⇒ 1.76515 | 37.3 | |
| 4.7291 ⇒ 2.36455 | 77.3 | |
| SFG, o + o ⇒ e | ||
| 1.3188 + 0.6594 ⇒ 0.4396 | 62.3 | |
| 1.3188 + 1.0642 ⇒ 0.5889 | 37.7 | |
| 4.7762 + 3.1841 ⇒ 1.9105 | 46.6 | |
| 5.2955 + 3.5303 ⇒ 2.1182 | 59.5 | |
| XZ Plane, φ = 0°, θ > Vz | ||
| SHG, o + o ⇒ e | ||
| 1.0642 ⇒ 0.5321 | 70.4 | |
| 1.3188 ⇒ 0.6594 | 56.8 | |
| 1.3382 ⇒ 0.6691 | 56.2 | |
| 3.5303 ⇒ 1.76515 | 58.8 | |
| SFG, o + o ⇒ e | ||
| 1.3188 + 1.0642 ⇒ 0.5889 | 62.6 | |
| 5.2955 + 3.5303 ⇒ 2.1182 | 86.1 | |
Experimental Value of Temperature Bandwidth at T=295K
| Interaction Wavelength[μm] | θexp [deg] | ΔT [◦C] |
| YZ Plane, φ = 90° | ||
| SHG, o + o ⇒ e | ||
| 1.0642 ⇒ 0.5321 | 46.4 | 0.39 |
| 1.3382 ⇒ 0.6691 | 29.7 | 0.59 |
| 3.5303 ⇒ 1.76515 | 37.1 | 2.3 |
| SFG, o + o ⇒ e | ||
| 5.2955 + 3.5303 ⇒ 2.1182 | 59.5 | 2.4 |
| XZ Plane, φ = 0°, θ >Vz | ||
| SHG, o + o ⇒ e | ||
| 1.0642 ⇒ 0.5321 | 71.4 | 0.77 |
| 1.3382 ⇒ 0.6691 | 56.2 | 2.2 |
| 3.5303 ⇒ 1.76515 | 58.1 | 10.1 |
Spectrum
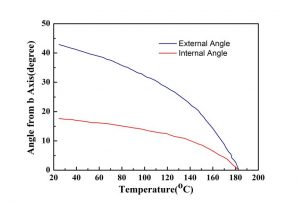 | 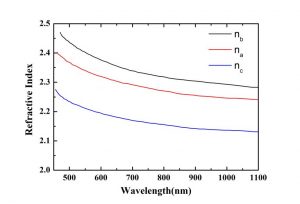 |
| KNbO3-Temperature variation of the supporting phase | Refractive index dispersion of KNbO3 at room temperature |
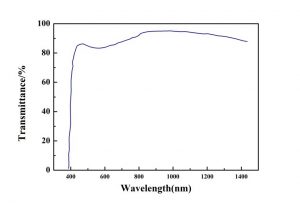 | 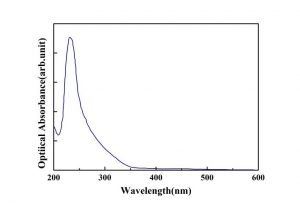 |
| KNbO3-Transmission Spectra | KNbO3-Optical Absorption |
References
| [1] Baudisch M , Hemmer M , Pires H , et al. Performance of MgO:PPLN, KTA, and KNbO3 for mid-wave infrared broadband parametric amplification at high average power[J]. Optics Letters, 2014, 39(20):5802-5. |
| [2] Kim J H , Yoon C S . Domain switching characteristics and fabrication of periodically poled potassium niobate for second-harmonic generation[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2002, 81(18):3332-3334. |
| [3] Zysset B , Biaggio I , Gunter P N . Refractive indices of orthorhombic KNbO3. I. Dispersion and temperature dependence[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 1992, 9(3). |
| [4] Umemura N , Yoshida K , Kato K . Phase-Matching Properties of KNbO_3 in the Mid-Infrared[J]. Applied Optics, 1999, 38(6):991-994. |
| [5] Uematsu Y . Nonlinear Optical Properties of KNbO3 Single Crystal in the Orthorhombic Phase[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1974, 13(9):1362-1368. |
| [6] Baumert J C , Hoffnagle J , Gunter P . Nonlinear Optical Effects In KNbO3 Crystals At AlxGa1_xAs, Dye, Ruby And Nd:YAG Laser Wavelengths.[C]// European Conference on Optics. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 1985. |
| [7] Yoshiguchi T , Ota T , Adachi N . Crystal Growth of KNbO 3 by Solution-Dropping Method[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2007, 544-545:697-700. |
| [8] Yamanouchi K , Wagatsuma Y , ODaGawa H , et al. Single crystal growth of KNbO3 and application to surface acoustic wave devices[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2001, 21(15):2791-2795. |
| [9] Shao-Yi, Yong-Qiang, Zhang, et al. First-principles study of structural, electronic, elastic, and optical properties of cubic KNbO3 and KTaO3 crystals[J]. Physica status solidi, B. Basic research, 2017, 254(5). |
| [10] Grabowska E . Selected perovskite oxides: Characterization, preparation and photocatalytic properties—A review[J]. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 2016, 186:97-126. |
| [11] Comes R , Lambert M , Guinier A . The chain structure of BaTiO3 and KNbO3[J]. Solid State Communications, 1968, 6(10):715-719. |
| [12] Zgonik M , Schlesser R , Biaggio I , et al. Materials constants of KNbO3 relevant for electro- and acousto-optics[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1993, 74(2):1287-1297. |
| [13] MD Fontana, Metrat G , Servoin J L , et al. Infrared spectroscopy in KNbO3 through the successive ferroelectric phase transitions[J]. Journal of Physics C Solid State Physics, 1984, 17(3):483-514. |
| [14] A, Magrez, E, et al. Growth of Single-Crystalline KNbO3 Nanostructures.[J]. ChemInform, 2006, 37(15):no-no. |
| [15] Tennery V J , Hang K W . Thermal and X‐Ray Diffraction Studies of the NaNbO3KNbO3 System[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1968, 39. |
| [16] Wu, Xing, and, et al. Progress in KNbO3 crystal growth[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1986, 78(3):431-437. |
| [17] Baumert J C , P Günter, Melchior H . High Efficiency Second Harmonic Generation in KNbO3 Crystals[J]. Optics Communications, 1983, 48(3):215-220. |
| [18] Currat R , Comes R , Dorner B , et al. Inelastic neutron scattering in orthorhombic KNbO3[J]. Journal of Physics C:Solid State Physics, 1974. |
| [19] Matthews D G , Conroy R S , Sinclair B D , et al. Blue microchip laser fabricated from Nd:YAG and KNbO3[J]. Optics Letters, 1996, 21(3):198-200. |
| [20] Krakauer H , Yu R , Wang C Z , et al. Dynamic local distortions in KNbO3[J]. Journal of Physics Condensed Matter, 1999, 11(18):3779. |
| [21] U, Flückiger, and, et al. On the preparation of pure, doped and reduced KNbO3 single crystals[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1978. |
| [22] Yang Y , Jung J H , Yun B K , et al. Flexible pyroelectric nanogenerators using a composite structure of lead-free KNbO(3) nanowires.[J]. Advanced Materials, 2012, 24(39):5357-5362. |
If you are intereted in KNbO3, please click the button below to enquire or ask for a samplel.
Related article(s) with KNbO3:
Related case study with KNbO3:
There is no related case study with this product, please visit case study page to find out more.
Related solution(s) with KNbO3:
There is no related application(s) with this product, please visit solutionspage to find out more.
Related video(s) with KNbO3:
There is no related video(s), please visit videos page to find out more.
