Introduction: Embracing The Laser Technology
With the modernization of healthcare, the utilization of laser glass in the medical field has catapulted to the forefront of surgical and dermatological advancements. The transformative impact of laser glass in procedures like laser surgery, dermatology, and aesthetic treatments has undeniably redefined the healthcare landscape.

Understanding Laser Glass and Its Medical Applications
The practical application of laser glass revolves around its core mechanism of operation – the lasing process. Laser glass, the heart of any laser system, houses the active medium where the lasing action occurs. When subjected to external energy, this medium absorbs it, which results in an excited state. As the energy dissipates, the medium emits light, and it’s this emitted light, when amplified, that forms the laser beam.
Intricacies of the Lasing Process
A better understanding of this process can be achieved by breaking it down into three fundamental steps: Absorption, Spontaneous Emission, and Stimulated Emission.
During Absorption, the laser medium, like erbium-doped or neodymium-doped glass, absorbs energy (pumped in via an external source) to reach an excited state.
In Spontaneous Emission, the excited medium naturally returns to its lower energy state, emitting light in the process.
Lastly, Stimulated Emission occurs when an incoming photon of the right energy level triggers the emission of a second, identical photon. These photons, traveling in unison, amplify to generate the laser beam.
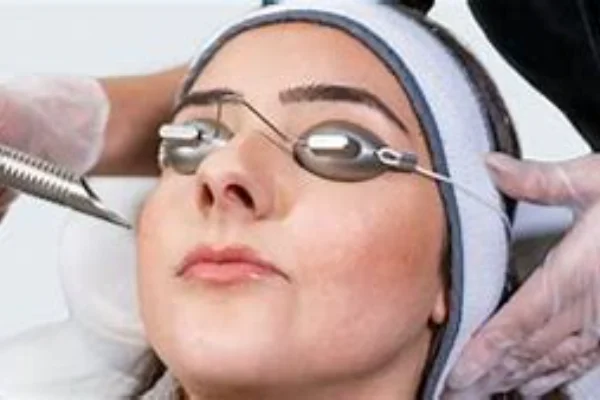
Medical Intervention with Laser Glass
In the medical arena, this amplified light beam translates to a high-precision, high-intensity tool for practitioners. It permits a degree of control unmatched by traditional surgical instruments, thus augmenting the potential for better patient outcomes. Let’s delve into some of the key medical applications that benefit from this technology:
1. Ophthalmology: Laser glasses have found their use in ophthalmic procedures such as LASIK and PRK for vision correction. They help in reshaping the cornea with great precision, leading to improved visual acuity.
2. Oncology: Laser glasses aid in the management of several cancer-related procedures, like photodynamic therapy. In such procedures, laser beams help activate specific drugs for the destruction of cancer cells.
3. Dentistry: In dentistry, the utilization of laser glass has transformed various treatments. From gum reshaping to tooth whitening and cavity treatment, lasers have facilitated pain-free and quick dental procedures.
4. Neurosurgery: Lasers have also found their place in neurosurgery for the treatment of brain tumors and other neurological conditions. The precision of lasers helps in reducing damage to the surrounding sensitive brain tissues.
Thus, laser glass, through its fundamental lasing mechanism, finds diverse medical applications, continuously pushing the boundaries of health intervention. This adaptable technology holds immense potential for further advancements, cementing its place in the future of medicine.
Laser glass, which acts as the heart of any laser system, houses the active laser medium. It has been instrumental in enhancing the efficacy and precision of various medical treatments and procedures, fostering minimal invasion and faster recovery periods.
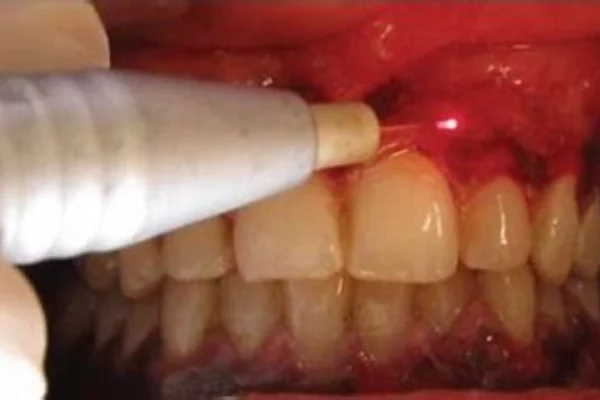
Laser Surgery
Laser surgery employs a finely focused laser beam, enabling precise control over the procedure. By adopting erbium-doped or neodymium-doped laser glass, surgeons can manipulate tissue interaction with minimal thermal damage—ultimately leading to better surgical outcomes.
Dermatology and Aesthetic Treatments
In the realm of dermatology and aesthetic treatments, laser glass has significantly improved the management and treatment of various skin conditions. The capabilities range from laser hair removal and scar reduction to the management of pigmentation disorders and anti-aging treatments.
Delving into the World of Laser Glass: An In-Depth Look at Erbium-Doped and Neodymium-Doped Glasses

As we venture deeper into the realm of laser glass and its significant impact on medical science, we discover two distinct and crucial types that have found immense application in the field – the Erbium-doped glass and the Neodymium-doped glass. Both these types offer unique capabilities and advantages, catalyzing remarkable advancements in medical procedures.
The Prowess of Erbium-Doped Glass
The science behind the Erbium-doped glass is fascinating. It all boils down to the atomic structure of Erbium (Er), a rare-earth element. When Erbium ions are incorporated into a glass matrix, they create an active medium that can emit light at specific wavelengths when pumped with energy.
Erbium-doped glass has the unique ability to emit laser light around the 1.5-micron wavelength, a range that is most compatible with human tissues. This compatibility permits greater absorption of the laser energy, providing an advantage in precision.
In addition to surgical procedures, Erbium-doped glass has gained traction in dermatology and aesthetic treatments. For instance, it is used in ablative laser resurfacing – a procedure that precisely removes the outer layers of aged or sun-damaged skin. The result is smoother, fresher skin with reduced lines and wrinkles.
The Erbium-doped glass is also employed in fractional laser treatments. These procedures involve treating a fraction of the skin’s surface, leaving surrounding tissues untouched for promoting rapid healing and reducing recovery time.

The Might of Neodymium-Doped Glass
The Neodymium-doped glass, on the other hand, is distinguished by its application in high-power laser systems. Neodymium (Nd) is another rare-earth element whose ions, when doped into glass, produce a powerful lasing medium. This laser glass is capable of storing high levels of energy and subsequently releasing it in the form of intense laser pulses.
One of the signature characteristics of Neodymium-doped glass is its high-energy output. The lasers produced can penetrate deeper into tissues, making them particularly effective in procedures that require high power, such as photocoagulation in ophthalmology and tattoo removal in dermatology.
Moreover, Neodymium-doped glass lasers find extensive use in hair removal treatments. Their ability to target the melanin in hair follicles without affecting the surrounding skin has revolutionized aesthetic treatments.
In the realm of dentistry, Neodymium-doped glass lasers have been used for gum disease treatment and tooth whitening, offering patients a more comfortable experience compared to traditional methods.
Reaping the Rewards: Unpacking the Multifaceted Benefits of Laser Glass in Medical Applications
Laser glass in medical applications has set in motion a new era of unprecedented advantages. From escalating precision in procedures to maximizing patient comfort, laser glass has woven an intricate tapestry of benefits that continues to revolutionize the field of medicine.
Elevating Precision in Treatment
One of the most appreciated benefits of laser glass is the enhanced precision it brings to medical treatments. With their ability to produce highly focused laser beams, they permit meticulous targeting of the treatment area. This fine-tuning results in significant improvement in surgical outcomes, while also reducing collateral damage to healthy tissues.
In the realm of ophthalmology, this elevated precision has ushered in a dramatic change. Procedures like LASIK and PRK that employ laser glass have made vision correction safer, more accurate, and less reliant on glasses or contact lenses.
Tailoring Energy Delivery
Laser glass holds the distinctive advantage of delivering energy with unparalleled accuracy. This precise energy delivery is critical in many procedures, such as in the removal of tumors or treatment of vascular conditions.
For instance, in endovenous laser treatment for varicose veins, the precise energy delivery of the laser glass is harnessed to collapse and seal off the affected veins. This targeted treatment reduces the risk of damaging surrounding tissues and ensures quicker recovery times for patients.
Enabling Minimally Invasive Procedures
Another laudable benefit of laser glass is its role in enabling minimally invasive procedures. Laser surgeries, with their high-precision and targeted approach, drastically reduce the need for large incisions. This translates into less surgical trauma, lower risk of infection, reduced scarring, and ultimately, quicker recovery times.
Take the case of laparoscopic surgeries, where laser glass plays a pivotal role. Surgeons can perform complex procedures through small incisions, reducing post-operative pain and enhancing the recovery process.
Reducing Thermal Damage
Traditional surgical procedures often carry the risk of thermal damage due to the use of hot surgical tools. Laser glass, in contrast, enables procedures that induce minimal thermal damage.
In dermatological treatments such as laser skin resurfacing, the risk of burns and thermal damage is significantly reduced. This ensures a safer procedure and minimizes post-treatment complications, such as hyperpigmentation.
Boosting Patient Comfort and Satisfaction
Ultimately, all these advantages of laser glass contribute to one crucial aspect – improving patient comfort and satisfaction. The prospects of less invasive procedures, lower post-operative pain, and quicker recovery times undoubtedly enhance the patient’s experience, leading to greater satisfaction.
Conclusion: The Bright Future of Laser Glass in Medical Applications
In the world of healthcare, the advancements in laser glass technology are rewriting the norms of surgical and dermatological treatments. Laser surgery, dermatology, and aesthetic treatments with laser glass have not only improved the quality of medical care but also enhanced patient comfort and convenience.
FAQs
- What is laser glass used for in medical applications?
- Laser glass is used in various medical applications like laser surgery, dermatology treatments, and aesthetic procedures. Its precision and minimal invasiveness are the primary reasons for its wide adoption.
- What are the advantages of erbium-doped and neodymium-doped laser glass in medical procedures?
- Erbium-doped laser glass offers precision and minimizes tissue damage, while neodymium-doped laser glass offers high-energy output and deep tissue penetration.
- How does laser glass benefit laser surgery?
- Laser glass enables precise energy delivery and optimized tissue interaction, minimizing thermal damage and promoting faster recovery.
- How does laser glass improve dermatological and aesthetic treatments?
- Laser glass improves dermatological and aesthetic treatments by providing targeted treatment, reducing damage to surrounding tissue, and ensuring quick recovery.
- What does the future hold for laser glass in medical applications?
- With continuous advancements, the future of laser glass in medical applications looks promising. It is set to further enhance the quality of medical care and patient comfort.

Frank
Frank graduated from the University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, majoring in optics. As a technical engineer at Crylink Company, he deeply understands crystal materials and laser components.
Related Video(s) with this Article
Related Product(s) with this Article
Related Application(s) with this Article
