In the world of gemstones, natural beauty has long been admired, but technological advancements have paved the way for the creation of artificial gemstones that rival their natural counterparts in terms of both aesthetics and durability. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the popular methods of growing artificial gemstones. From the Czochralski method to the Bridgman process, we will delve into the fascinating world of synthetic gemstone production.
Chapter 1: Understanding the Appeal of Artificial Gemstones
The Allure of Synthetic Gemstones
In recent years, synthetic gemstones have experienced an unprecedented surge in popularity, captivating the hearts of jewelry enthusiasts and gemstone aficionados worldwide. The allure of lab-grown gems is multifaceted, rooted in a combination of factors that have made them an increasingly preferred choice for those seeking exquisite gemstones for their jewelry collections.

Affordability: One of the most compelling aspects of synthetic gemstones is their affordability. Unlike their natural counterparts, which often come with hefty price tags due to their rarity and mining-associated costs, lab-grown gems offer a cost-effective alternative. This affordability democratizes gemstone ownership, allowing a broader audience to enjoy the beauty and elegance of gemstone-adorned jewelry.
Ethical Sourcing: Synthetic gemstones come with an ethical advantage that resonates with conscious consumers. These gems are cultivated within controlled laboratory environments, eliminating concerns related to unethical mining practices, such as environmental degradation and exploitative labor. Choosing lab-grown gems aligns with the values of ethical sourcing and sustainability, making them an ethically sound choice.
Exceptional Visual Appeal: Lab-grown gemstones are celebrated for their exceptional visual appeal. They exhibit the same dazzling brilliance, captivating colors, and optical properties that make natural gemstones so alluring. Whether it’s a vibrant ruby or a sparkling diamond, synthetic gemstones hold their own in terms of beauty and aesthetic value.
As we delve deeper into the world of artificial gemstones, we will continue to unveil the myriad reasons behind their burgeoning popularity. From the accessibility that affordability offers to the ethical consciousness they embody, synthetic gemstones stand as a compelling alternative in the realm of jewelry and aesthetics.
Chapter 2: Czochralski Method: Creating Gemstone Magic
The Czochralski Process Explained
At the heart of the synthetic gemstone revolution lies the Czochralski method, affectionately known as the CZ process. This section offers a detailed exploration of the intricacies of this renowned technique and how it conjures the magic necessary to produce high-quality gemstones.
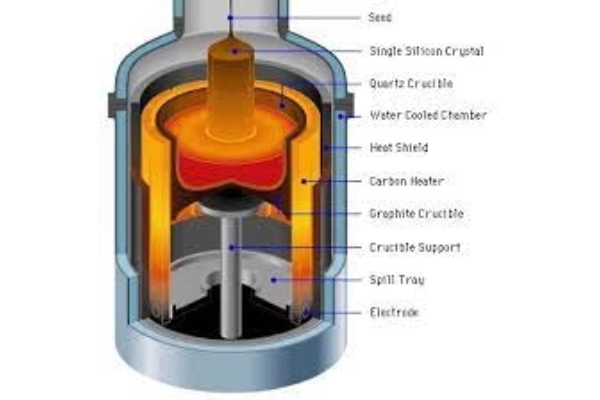
Crystal Growth: The Czochralski method hinges on the principle of crystal growth from a melt. A seed crystal is delicately lowered into a molten material, which can be composed of elements such as corundum for sapphires. As the seed crystal is slowly lifted, it draws material from the molten substance. As this material solidifies, it forms a single crystal structure. The controlled environment, including temperature and cooling rate, is crucial to achieving the desired gemstone quality.
Quality Control: The precision of the Czochralski method enables rigorous quality control. By carefully adjusting factors such as temperature, cooling rate, and material composition, gem growers can fine-tune the crystal’s characteristics. This fine-tuning ensures that the resulting gemstone meets the desired standards for attributes like color, clarity, and size.
Versatile Applications: Gemstones produced through the Czochralski method find their applications across diverse industries. They shine brilliantly in the jewelry sector, gracing engagement rings, necklaces, and earrings with their captivating hues. Moreover, their exceptional optical properties make them invaluable in advanced optics, contributing to the creation of precision lenses, prisms, and waveplates.
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of the Czochralski method, we unlock the secrets behind its ability to create gemstone magic. The controlled environment and meticulous craftsmanship of this technique contribute to the allure of lab-grown gemstones, setting them apart as a remarkable choice in both aesthetics and technology.
Applications of Czochralski-Grown Gemstones
Exploring the Versatility of Czochralski-Grown Gemstones
The gemstones cultivated through the Czochralski method are versatile marvels, finding their place in a multitude of applications across various industries.
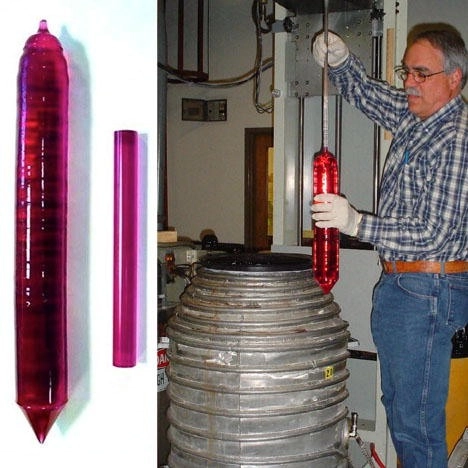

Stunning Jewelry: Czochralski-grown gemstones, with their impeccable clarity, vibrant colors, and exceptional brilliance, are celebrated in the world of jewelry. They grace engagement rings, necklaces, and earrings, adding a touch of elegance to every piece. Whether it’s a deep blue sapphire or a fiery ruby, these gemstones hold their own in the realm of adornment.
Advanced Optics: The precision and optical properties of Czochralski-grown gemstones extend their influence into the realm of advanced optics. These gemstones serve as key components in precision lenses, prisms, and waveplates used in scientific instruments, laser systems, and telecommunications equipment. Their ability to transmit, refract, and reflect light with precision makes them indispensable in enhancing optical systems’ performance.
Decorative Pieces: Beyond their traditional roles, Czochralski-grown gemstones also find their way into decorative items and collectibles. Their captivating beauty and versatility make them a choice material for crafting ornamental pieces that delight art enthusiasts and collectors alike.
The applications of gemstones grown through the Czochralski method underscore their versatility and the extraordinary value they bring to diverse industries. Whether adorning fingers, enhancing optical precision, or gracing decorative creations, these gemstones continue to showcase their brilliance and adaptability, cementing their status as gems of choice in the modern world.
Chapter 3: Bridgman Process: Crafting Gems with Precision
Unveiling the Bridgman Technique
In the world of synthetic gemstone production, the Bridgman process stands as a distinguished method known for its precision and quality. This chapter embarks on a journey into the intricate details of the Bridgman technique, shedding light on how it plays a crucial role in the manufacturing of high-quality gemstones.
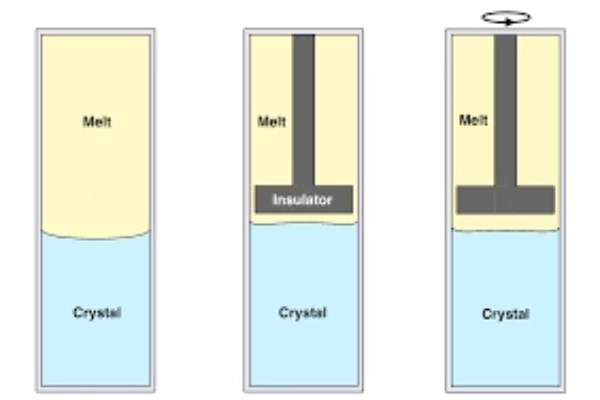
Crystal Growth Mastery: The Bridgman process revolves around the art of crystal growth, emphasizing controlled and meticulous techniques. Seed crystals are carefully immersed into a melt, where they gradually ascend, drawing material from the molten medium. This gradual ascent, guided by precise temperature and cooling adjustments, leads to the formation of a single crystal structure of remarkable quality.
Quality Assurance: One of the distinguishing features of the Bridgman process is its commitment to stringent quality control. By fine-tuning critical factors such as temperature gradients, crucible design, and material purity, gemstone growers can exercise exceptional control over the resulting gem’s characteristics. This fine-tuning ensures that the gemstone exhibits the desired attributes, including clarity, color, and size.
Advantages of Bridgman-Grown Gemstones
The advantages of gemstones cultivated through the Bridgman process are manifold, making them highly sought-after in various industries. This section explores the unique attributes and applications of Bridgman-grown gemstones.
Scientific Instruments: Bridgman-grown gemstones find a niche in scientific instruments, where their optical clarity and precision play pivotal roles. These gemstones are used as optical components in various analytical and research instruments, contributing to the advancement of science.
Laser Technology: The exceptional optical properties of Bridgman-grown gemstones make them ideal candidates for use in laser technology. They serve as gain media in solid-state lasers, amplifying and emitting laser light with precision. This application is crucial in fields such as medical devices, industrial processes, and military equipment.
As we delve deeper into the Bridgman process, we uncover the artistry and precision involved in creating gemstones that excel in scientific precision and technological innovation. The controlled environment and meticulous craftsmanship of this method have positioned Bridgman-grown gemstones as gems of choice in advanced applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the world of synthetic gemstone production is a captivating blend of science, technology, and artistry. The methods discussed in this article, from the Czochralski process to the Bridgman technique and hydrothermal growth, offer diverse options for creating exquisite gemstones that cater to various preferences and purposes.
FAQs
- Q1: Are synthetic gemstones as valuable as natural ones?
- A1: The value of synthetic gemstones depends on factors such as quality, rarity, and market demand. While they are more affordable, they may not carry the same intrinsic value as certain natural gems.
- Q2: Are there ethical concerns surrounding synthetic gemstone production?
- A2: Synthetic gemstone production is generally considered more ethical than some aspects of natural gem mining, as it reduces environmental impact and avoids issues like “blood diamonds.”
- Q3: What is the difference between hydrothermal and Czochralski gemstones?
- A3: Hydrothermal gemstones are grown using high-pressure, high-temperature conditions, while Czochralski gemstones are produced through a crystallization process from molten materials. The two methods yield gemstones with slightly different characteristics.
- Q4: Can synthetic gemstones be used for engagement rings?
- A4: Yes, many people choose synthetic gemstones for engagement rings due to their affordability and visual appeal. They can be an ethical and cost-effective choice.
- Q5: Are there any gemstone collectors who prefer synthetic gems over natural ones?
- A5: Yes, some collectors appreciate the craftsmanship and uniqueness of synthetic gemstones, and they actively seek them out to add to their collections.

Frank
Frank graduated from the University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, majoring in optics. As a technical engineer at Crylink Company, he deeply understands crystal materials and laser components.
Related Video(s) with this Article
Related Product(s) with this Article
Related Application(s) with this Article
